Humans have been enjoying chocolate since prehistoric times. The earliest known evidence of chocolate dates back 5,300 years ago, in traces of cacao found in pottery used by the Mayo-Chinchipe culture in the highlands of what is now Ecuador. Cacao was a cultural cornerstone of ancient Mayan culture. It was used as a currency, a sign of status, and as a food believed to be a gift from the gods.
Today, we know chocolate as a smooth, sweet confection, but the earliest known preparations were very different. The wealthy enjoyed a bitter drink made with chili peppers, vanilla, and other spices while commoners ate cacao mixed into porridge. Cacao eventually spread to Europe in the 1500s, brought over by Spanish colonizers, where it became a popular, sugar-sweetened beverage among aristocrats.
Chocolate bars didn’t come around until around the middle of the 19th century. The invention of a machine called the cocoa press allowed people to separate the roasted bean from the butter. In 1847 in Bristol, UK, chocolatier J.S. Fry & Sons made the first chocolate bar. Compared to the confection that we know today, it was dry and bitter. But it would kick off the world’s love for chocolate bars. In 1875, the world’s first milk chocolate bar was produced in Switzerland, offering a creamier, more palatable sweet than the first-ever chocolate bars. Just over two decades later in 1897, Cadbury launched its first milk chocolate bar. And so the story goes.
 Taza
Taza
What is vegan chocolate?
Vegan chocolate is any chocolate that’s made without animal products. The main ingredients in your standard chocolate bar are cocoa beans, sugar, and cocoa butter. Generally, milk is the only non-vegan ingredient that you’ll find in chocolate. Most chocolate is sweetened with sugar (sugar-free options contain monk fruit, stevia, or other alternative sweeteners), so your chances of finding honey are very slim. Even dark chocolate can contain milk, so it never hurts to read the ingredient list.
 Nohmad
Nohmad
Is vegan chocolate ethical?
Sad to say, but vegan chocolate isn’t necessarily ethical.
Even if a chocolate bar is free from animal products, journalists have documented the widespread use of child labor and slavery on cocoa farms in West African countries, which supply the majority of the world’s chocolate. This includes some of the industry’s biggest names. Europeans brought cocoa to this region so they could establish farms where labor was cheap or free, according to the Food Empowerment Project (FEP), a vegan food justice nonprofit.
BECOME A VEGNEWS VIP: Get exclusive product deals, freebies, and perks galore!
Unfortunately, not even fair-trade and the Rainforest Alliance certifications are a 100-percent guarantee that chocolate was made without child labor.
What’s in vegan milk chocolate?
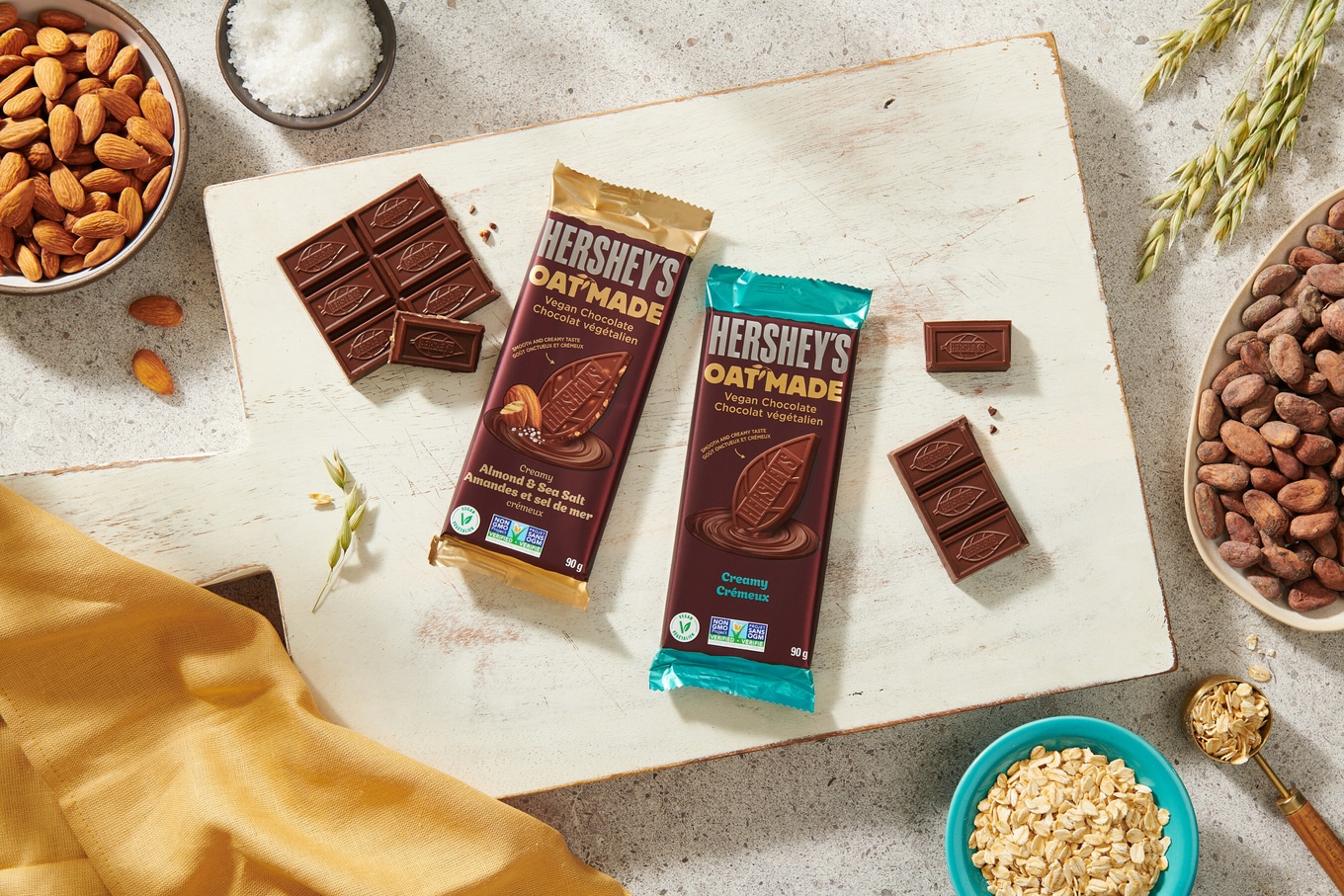
Dark chocolate used to be just about the only dairy-free chocolate option out there. But, that’s no longer the case. The vegan chocolate market is booming and cocoa heavyweights such as Hershey’s, Cadbury, and Lindt have rolled out dairy-free milk chocolate bars. And, there are plenty more brands to choose from. These brands are making vegan milk chocolate bars from a multitude of plant-based milks, including oat, coconut, rice, and almond. Vego, a 100-percent vegan brand, blends hazelnut butter into its bars to create a creamy, melt-in-your-mouth texture, for example.
Vegan milk chocolate bars
- 7th Heaven
- Break Free Candy
- Happi Choc
- Hershey’s
- LoveRaw
- LOVO Chocolate
- Moo Free
- No Whey! Foods
- Ombar
- Rad Chocolate
- Rawmio
- Taza Chocolate
- TCHO
- Trader Joe’s
- Vego
- VGAN Chocolate
Vegan dark chocolate bars
- Alter Eco
- Amore di Mona
- Askinosie Chocolate
- Beyond Good
- Bixby & Co.
- Chocolove
- Compartes
- Divine Chocolate
- Elements
- Endangered Species
- Equal Exchange
- Ghirardelli
- Green & Black’s
- Happy by Chocolate Inspirations
- Hu Kitchen
- Lake Champlain Chocolates
- Lily’s
- Magic Chocolate
- Moo Free
- Montezuma’s
- Ombar
- Pascha Chocolate
- Raaka
- Rad Chocolate
- Ragged Coast Chocolates
- Rawmio
- Ritter Sport
- Taza Chocolate
- TCHO
- Theo Chocolate
- Tony’s Chocolonely
- Trader Joe’s
- VGAN Chocolate
- Vosges
Vego
Vegan white chocolate
- 7th Heaven
- Go Max Go
- Happi Choc
- iChoc
- King David
- Lagusta’s Luscious
- LoveRaw
- Moo Free
- No Whey! Foods
- Pascha Chocolate
- Plamil
- TCHO
- Vego
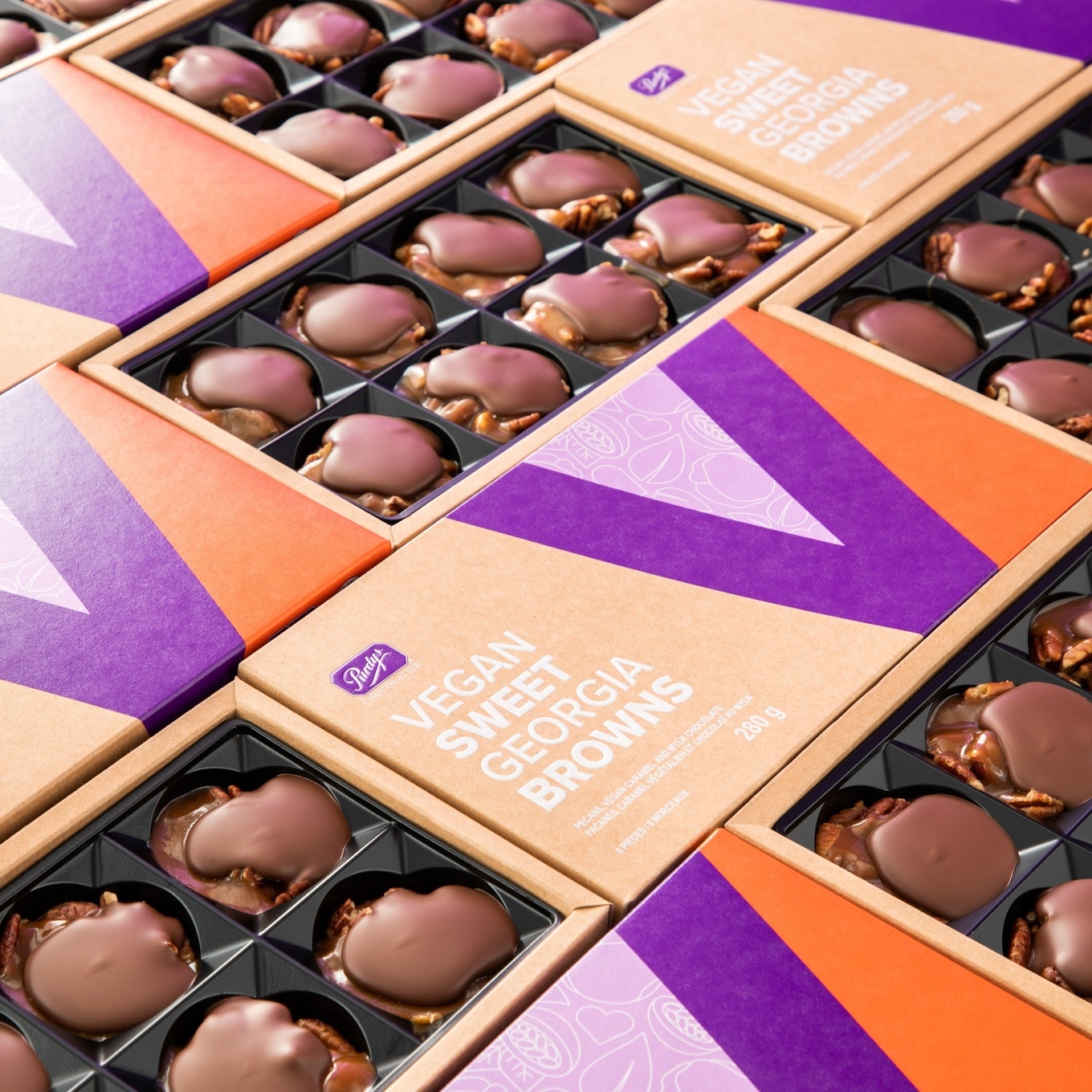
Purdys
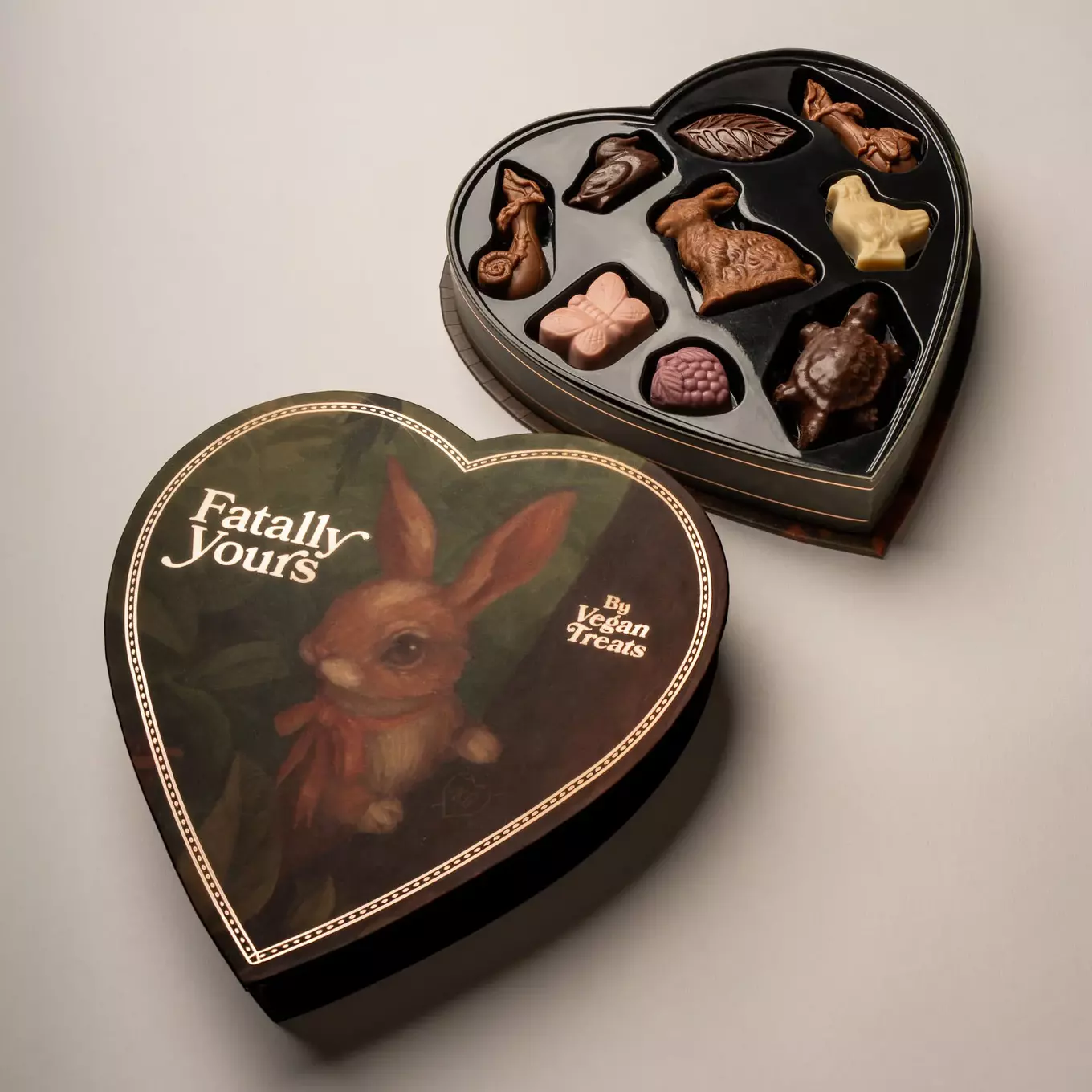
Vegan truffles and bonbons
- Compartés
- Dallman Confections
- Good Girl Chocolate
- Lagusta’s Luscious
- Lake Champlain Chocolates
- LoveRaw
- Montezuma’s
- No Whey! Foods
- Purdys
- Ragged Coast Chocolates
- Vosges
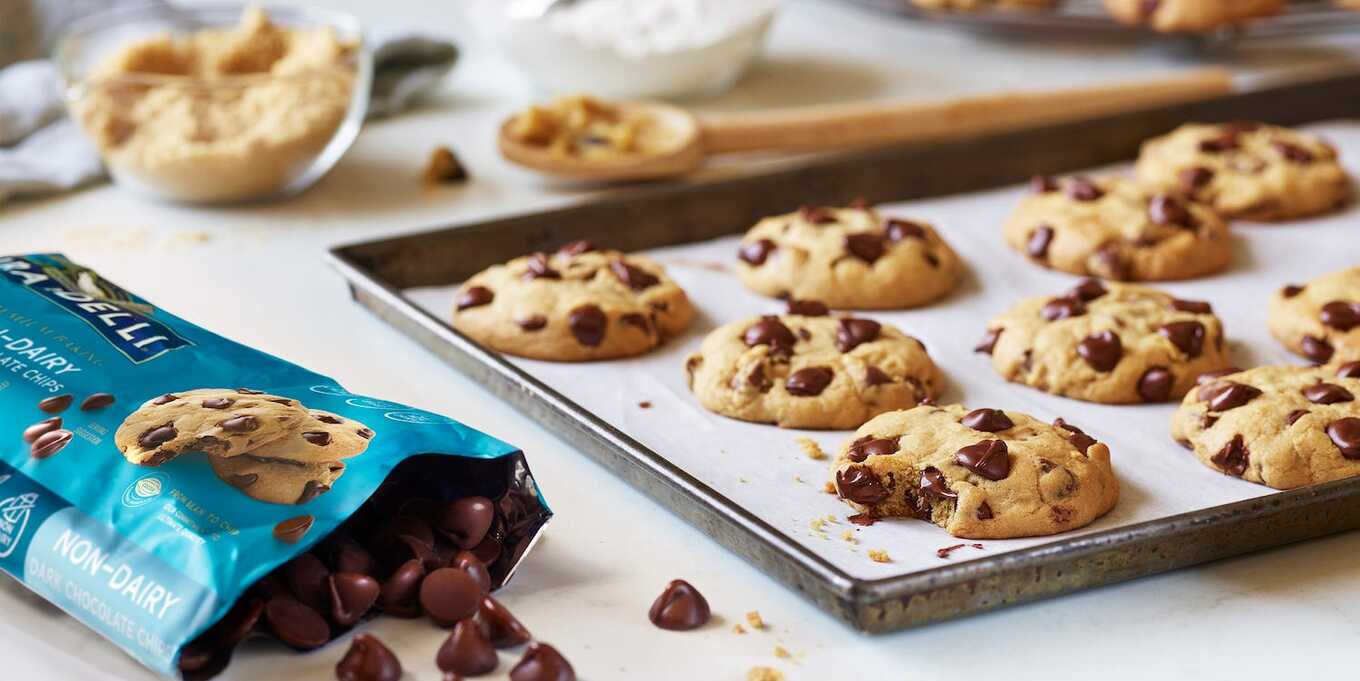
Vegan chocolate chips
- Baker’s Choice
- Dee Best
- Enjoy Life Foods
- Equal Exchange
- Ghirardelli
- Hu Kitchen
- King David
- Lily’s
- Nestle Toll House
- Pascha Chocolate
- Simple Truth
- Supernatural
For more vegan guides, read:
JUMP TO ... Latest News | Recipes | Guides | Health | Subscribe
Here at VegNews, we live and breathe the plant-based lifestyle, and only recommend products we feel make our lives amazing. Occasionally, articles may include shopping links where we might earn a small commission, but in no way does this effect the editorial integrity of VegNews.